Product Details
| Species Reactivity |
Rat (Rattus norvegicus) |
| UniProt |
|
| Abbreviation |
DKK1 |
| Alternative Names |
DKK-1; SK; dickkopf homolog 1|dickkopf related protein-1|dickkopf-1 like |
| Range |
Request Information |
| Sensitivity |
Request Information |
| Sample Type |
Serum, Plasma, Other biological fluids |
| Detection Method |
Sandwich |
| Analysis Method |
Quantitive |
| Assay Duration |
1-4.5h |
| Sample Volume |
1-200 μL |
| Detection Wavelengt |
450 nm |
Test principle
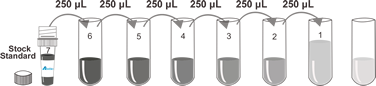
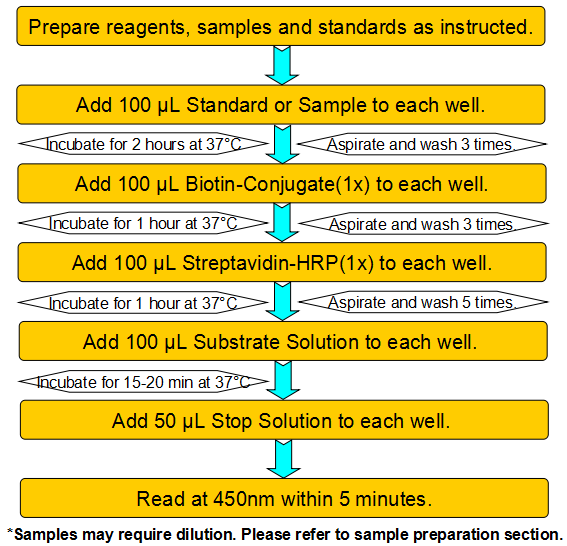
This assay employs a two-site sandwich ELISA to quantitate DKK1 in samples. An antibody specific for DKK1 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any DKK1 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After removing any unbound substances, a biotin-conjugated antibody specific for DKK1 is added to the wells. After washing, Streptavidin conjugated Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound avidin-enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of DKK1 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Product Overview
Dickkopf-related protein 1 is a protein that is a member of the dickkopf family. It is a secreted protein with two cysteine rich regions and is involved in embryonic development through its inhibition of the WNT signaling pathway. Elevated levels of DKK1 in bone marrow plasma and peripheral blood is associated with the presence of osteolytic bone lesions in patients with multiple myeloma. Sequence analysis predicted that the 266-amino acid DKK1 protein contains a 31-amino acid N-terminal signal peptide, 2 clusters of cysteine residues, and a potential C-terminal N-glycosylation site. SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis demonstrated that DKK1 is expressed as a 35-kD doublet protein, which is larger than the deduced molecular mass of 26 kD.
Components
Reagents |
Quantity |
Reagents |
Quantity |
Assay plate (96 Wells) |
1 |
Instruction manual |
1 |
Standard (lyophilized) |
2 |
Sample Diluent |
1 x 20 mL |
Biotin-Conjugate (concentrate 100 x) |
1 x 120 μL |
Biotin-Conjugate Diluent |
1 x 12 mL |
Streptavidin-HRP (concentrate 100 x) |
1 x 120 μL |
Streptavidin-HRP Diluent |
1 x 12 mL |
Wash Buffer (concentrate 25 x) |
1 x 20 mL |
Substrate Solution |
1 x 10 mL |
Stop Solution |
1 x 6 mL |
Adhesive Films |
4 |
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Rat DKK1. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Rat DKK1 and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Rat DKK1 and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Rat DKK1 in samples.
Sample Type |
Number |
Recovery range (%) |
Average(%) |
Serum |
10 |
90-101 |
96 |
EDTA plasma |
10 |
89-97 |
93 |
Heparin plasma |
10 |
91-99 |
95 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay)
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays)
Three samples of known concentration were tested in forty separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
CV (%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<8%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Rat DKK1 and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
Sample Type |
1:2 |
1:4 |
1:8 |
1:16 |
Serum |
78-89% |
81-99% |
92-103% |
95-105% |
EDTA plasma |
91-101% |
90-98% |
93-101% |
91-98% |
Heparin plasma |
92-103% |
93-102% |
92-99% |
91-101% |
Stability
The stability of ELISA kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test. Keep the kit at 37°C for 4 and 7 days, and compare O.D.values of the kit kept at 37°C with that of at recommended temperature. (referring from China Biological Products Standard, which was calculated by the Arrhenius equation. For ELISA kit, 4 days storage at 37°C can be considered as 6 months at 2 - 8°C, which means 7 days at 37°C equaling 12 months at 2 - 8°C).
Sample collection and storage
Serum: Use a serum separator tube (SST) and allow samples to clot for two hours at room temperature or overnight at 2 - 8°C before centrifugation for 15 minutes at 1000 × g. Remove serum and assay immediately or aliquot and store samples at ≤ -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Plasma: Collect plasma using EDTA, or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge for 15 minutes at 1000 × g at 2 - 8°C within 30 minutes of collection. Assay immediately or aliquot and store samples at ≤ -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Other biological fluids: Centrifuge samples for 20 minutes at 1000 × g. Remove particulates and assay immediately or store samples in aliquot at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Kits storage instructions
Store at 2-8°C. Please refer to Instruction Manual.