Current Position:Home>>ELISA Kit>> Fish Vitellogenin (VTG) ELISA Kit
Cat.No.: AE33313FI
Welcome to order from local distributors.
Add to cart Bulk requestFor research use only. Order now, ship in 3-5 days
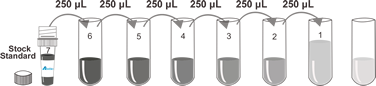
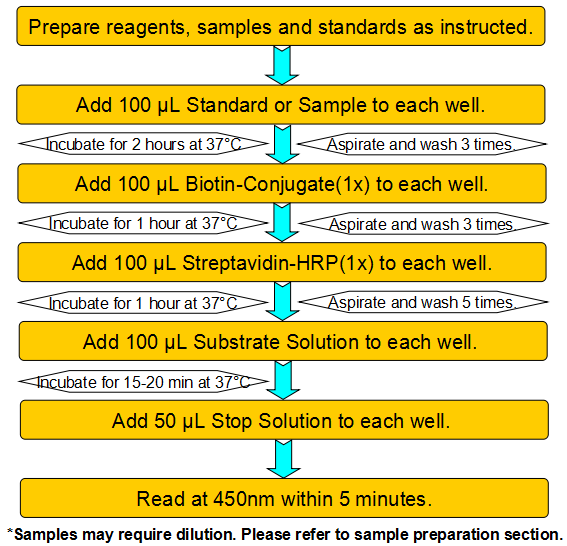

| Species Reactivity | Fish |
| UniProt | N/A |
| Abbreviation | VTG |
| Alternative Names | N/A |
| Range | 60-2000 ng/mL |
| Sensitivity | 60 ng/mL |
| Sample Type | Serum, Plasma, Other biological fluids |
| Detection Method | Competitive ELISA |
| Analysis Method | Quantitive |
| Assay Duration | 1-3h |
| Sample Volume | 1-200 μL |
| Detection Wavelengt | 450 nm |
Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
Assay plate (96 Wells) | 1 | Instruction manual | 1 |
Standard | 6 x 0.5 mL | Antibody | 1 x 6 mL |
HRP-Conjugate | 1 x 6 mL | Wash Buffer (concentrate 20 x) | 1 x 15 mL |
Substrate A | 1 x 7 mL | Streptavidin-HRP Diluent | 1 x 7 mL |
Stop Solution | 1 x 7 mL | Adhesive Films | 4 |